DM-J4340-2EC (24V) 9NM Joint Motor + USB to CAN Module + Power Adapter Board + Two-ended Cable
Motor Features:- Two encoders: single-turn absolute position of the output shaft. Not afraid of losing the absolute position of the output shaft when the power is off.
- Integrated design of motor and driver: compact structure and high integration.
- Supports visual debugging via an host computer. Firmware upgrade is supported.
- Motor speed, position, torque and motor temperature can be fed back through the CAN bus.
- It has double temperature protection function.
- Supports trapezoidal acceleration and deceleration in position mode.
Attention:1. Please use the motor in strict accordance with the specified working environment and the maximum allowable temperature range of the winding, otherwise it will cause permanent irreversible damage to the product.
2. Avoid debris from entering the rotor, otherwise it will cause the rotor to run abnormally.
3. Before use, check whether the parts are in good condition. If there are missing parts, aging, damage, etc., please stop using this product.
4. Make sure it's wired correctly. The motor is installed correctly and securely.
5. Do not touch the electronic rotor part when it is in use to avoid accidents. When the torque is high, the motor will heat up, so please be careful not to get burned.
6. Do not disassemble the motor, otherwise it will affect the control accuracy of the motor, and even cause the motor to run abnormally.
Package Included:- 1 x Motor (including drive)
- 1 x Power cable (including CAN communication terminal): XT30 (2+2)-F plug connection cable
- 1 x Debugging serial signal cable: GH1.25 connection cable-3pin
- 1 x USB to CAN module
- 1 x Power adapter board
- 1 x Two-ended cable
Packaging Details:- Weight: 0.65kg


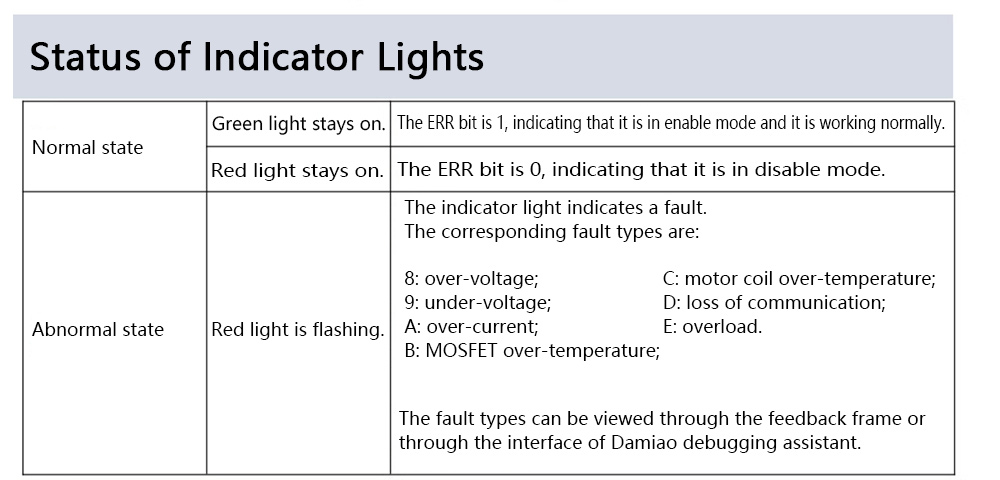 Working Modes:
Working Modes:*
MIT Mode: The MIT mode is designed to be compatible with the original
MIT mode. Allowing for seamless switching, this mode allows you to set
control ranges (P_MAX, V_MAX and T_MAX) in a flexible way. Your ESC
converts the received CAN data into control variables and calculates the
torque value as the current of the current loop. And the current loop
finally reaches the given torque current according to its adjustment
law.
* Speed Mode
* Position Mode


 5DOF Low Cost Robot Arm ROS Open Source Robotic Arm (Slave Arm) with XL430-W250-T Servo Motors
$551.16
5DOF Low Cost Robot Arm ROS Open Source Robotic Arm (Slave Arm) with XL430-W250-T Servo Motors
$551.16
 5DOF Low Cost Robot Arm ROS Open Source Robotic Arm (Master Arm) with XL330-077-T Servo Motors
$457.01
5DOF Low Cost Robot Arm ROS Open Source Robotic Arm (Master Arm) with XL330-077-T Servo Motors
$457.01
 Low Cost Robot Arm ROS Open Source Robotic Arm (5DOF Master Arm + 5DOF Slave Arm) with Servo Motors
$1,005.56
Low Cost Robot Arm ROS Open Source Robotic Arm (5DOF Master Arm + 5DOF Slave Arm) with Servo Motors
$1,005.56



